
La tortue a pitié, mais pas de lait (Proverbe Herero – Namibie).
The turtle has compassion, but no milk (Herero proverb – Namibia).
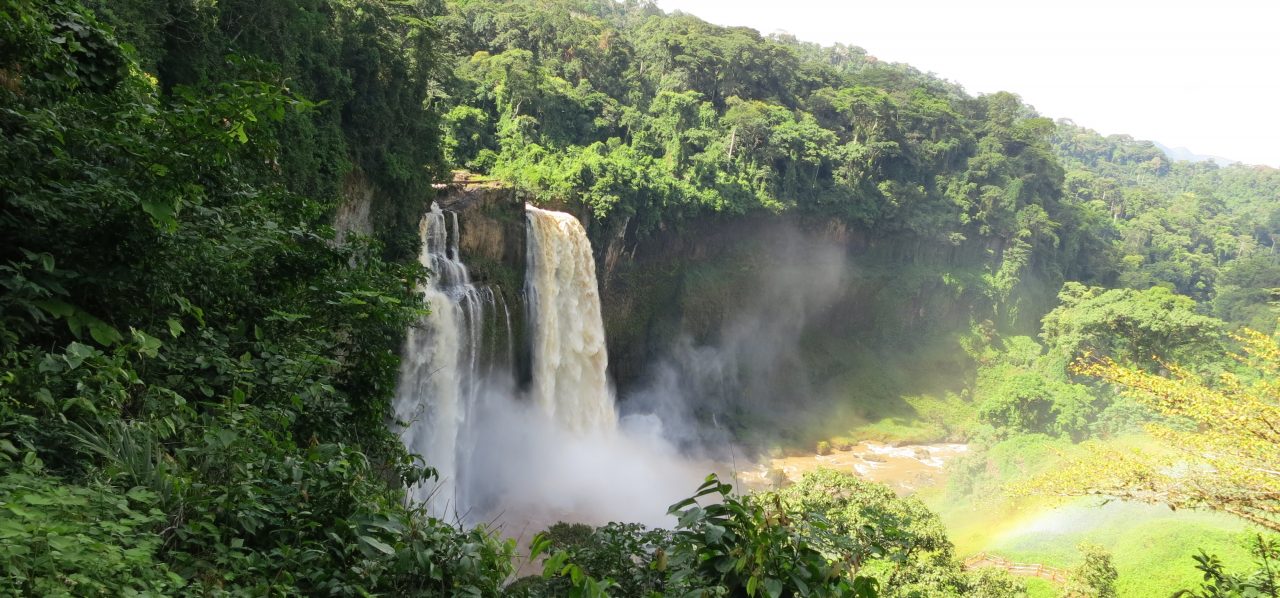


I found this Jacobin article which focuses on Rosa Luxemburg, a Polish Jewish revolutionary activist who exposed Germany’s genocide in what was then German South West Africa. She said, in her essay “Proletarian Women” (1912):
The workshop of the future requires many hands and hearts. A world of female misery is waiting for relief. The wife of the peasant moans as she nearly collapses under life’s burdens. In German Africa, in the Kalahari Desert, the bones of defenseless Herero women are bleaching in the sun, hunted down by a band of German soldiers and subjected to a horrific death of hunger and thirst. …
Three years later, she again recalled the litany of colonial crimes in her famous Junius Pamphlet:
The present world war is a turning point in the course of imperialism . . . The “civilized world” that has stood calmly by when this same imperialism doomed tens of thousands of Hereros to destruction; when the desert of Kalahari shuddered with the insane cry of the thirsty and the rattling breath of the dying . . . when in Tripoli the Arabs were mowed down, with fire and swords, under the yoke of capital while their civilization and their homes were razed to the ground.
Please check out the article on the Jacobin website to read more about this woman activist who at a time when very few could talk, she denounced the genocide perpetrated by German forces in Africa, particularly in Namibia. She pointed out that the “civilized world” stood by when atrocities were committed in Namibia… it seems like history has repeated itself around the globe for the past century with atrocities perpetrated in many places, while the civilized world or international community has stood by doing nothing or sometimes lending a hand to those perpetrating it. Like Rosa Luxemburg, let’s not turn a blind eye… let’s be part of the solution, and not the problem.

Last week, the Victoria & Albert Museum (V&A) and the British Museum “returned” some artifacts looted from the Ashanti Kingdom in modern-day Ghana, after over 150 years. When one reads the headlines in the news, one can only clap, until learning that this is a “long-term loan“! Wait! What? About 32 gold and silver items which had been stolen from the court of the Asantehene (Asante king) in the 19th century, have been sent on a long-term loan back to the Asante court. First, how long is a “long-term loan”? Second, why is it a loan, when these objects were looted from the Asantehene’s court back in the 19th century? They were not gifted, they were not sold, they were STOLEN! And to top it off, there has been a chief negotiator on the Ghanaian side to ensure that the objects will be in safe hands in Ghana! What? So, these objects do not belong to Ghanaians, and if something were to happen to these Ghanaian objects that were stolen by the British but are now hosted in British museums while on Ghanaian soil on long-term loan, then one can only bet that the British would make the Ghanaians pay for something that is theirs! Which world are we living in? Knowing the treacherous nature of these people, who is to say that they will not orchestrate a new theft of these objects so as to further deepen the debts under which Ghanaians are already crumbling? Actually, long-term in this case means 3 years, with the option of renewing for 3 years! This loan is probably not even free! Why, oh why, do we, Africans, agree to such deals?
Read for yourself… excerpts from the BBC
=====

The UK has returned [how can it be called return when it is a loan?] dozens of artefacts looted from what is today Ghana – more than 150 years after they were taken [i.e. stolen].
Some 32 gold and silver items have been sent on long-term loan to the country by the Victoria & Albert Museum (V&A) and the British Museum.
They were stolen from the court of the Asante king, known as the Asantehene, during 19th century conflicts between the British and powerful Asante people.
The objects are expected to be returned [loaned – see how the writer of this piece wants to create confusion in our minds?] to the current king on Friday.
His chief negotiator, Ivor Agyeman-Duah, told the BBC that the objects are currently in “safe hands” in Ghana ahead of them being formally received. They are due to go on display next month at the Manhyia Palace Museum in Kumasi, the capital of the Ashanti region, as part of celebrations to mark the silver jubilee of the current Asante King Otumfuo Osei Tutu II.

… Among the returned artefacts are a gold peace pipe, a sword of state and gold badges worn by officials charged with cleansing the soul of the king. The gold artefacts are the ultimate symbol of the Asante royal government and are believed to be invested with the spirits of former Asante kings.
The Asante people built what was once one of the most powerful and formidable states in west Africa – trading in, among others, gold, textiles and enslaved people. The kingdom was famed for its military might and wealth.

About a month ago, we saw the government of Niger revoke military accords with the United States, and ordering the US withdrawal of its military personnel and drone base from Niger [Niger suspends military “cooperation” with the US, effective immediately]. Among Niger’s grievances, were the non-respect of Niger, but above all was a treaty imposed upon Niger by the US to implant their largest drone base in the country. The spokesman of Niger’s government, Colonel Amadou Abdramane, exposed the fact that the military “cooperation” with the US was not even a real one, i.e. the US had installed their largest drone base in Africa, and possibly in the world, in Niger via a verbal agreement only, and the Niger people had to pay for the American base in their country, while the Americans never raised a hand to help Niger fight against the terrorist attacks that were maiming their citizens.
We have previously discussed here, on Afrolegends.com, other treaties signed during colonial era in the Liptako, Zinder, and Gaya regions of Niger between the French and the local kingdoms (mostly under duress). We have found the above-mentioned treaty between Niger and the US, and it is only about 13-pages long, more like 10, and really reminiscent of colonial era treaties that have no respect for the local governments and impose upon them unfair rules.
In the July 6, 2012 treaty between the US and Niger, US citizens are subject to American laws, and the government of Niger has no power over them on Niger soil, so if for instance, an American citizen hurts or kills a Niger citizen on Niger’s soil, s/he will face no retribution about this from Niger. They do not pay taxes to the country. While reading, it is understood that this document was unilaterally and entirely written by the American side; no accord, agreement/discussion went in front of the Niger parliament. By the way, guess who was the Niger counterpart who signed this traitorous document? Mohamed Bazoum who was, back then under President Mahamadou Issoufou, Minister of Foreign Affairs… Both puppets signed the document … do you understand now why all these foreign powers have been screaming and begging for the return of Bazoum to office?
In the document, the American army makes Niger foot the bills for all American army vehicles and planes that enter the Niger’s airspace. There is no sharing of information with the Niger government who does not know the exact number of American troops on its soil, or the number of its drones, or the equipment, etc. More importantly, there is no obligation of support from the US to Niger in its fight against the terrorism that has engulfed Niger’s northern territories for several years.
In summary, someone installs a base on your territory, you have no say about it; as one of the poorest countries on earth, you have to foot the bills for his planes entering your territory; this someone is not subject to your laws, taxes, and looks the other way as you are mired in a conflict for your survival; yet this someone has installed a military force or your soil! How is this not reminiscent of colonial treaties? How fair is it? As you read this treaty, what is Niger’s gain in it? Are these treaties always outrageous like that, or is it just in Africa?
Excerpts below are from the full document found on the US Department of State website.
=====

The Embassy of the United States of America presents its compliments to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Cooperation, African Integration, and Nigeriens Abroad of the Republic of Niger, and has the honor to refer to recent discussions between representatives of, our two Governments regarding issues related to United States military and civilian personnel …
… As a result Of these discussions, the Embassy proposes that United States personnel be accorded the privileges, exemptions, and immunities equivalent to those accorded to the administrative and technical staff of a diplomatic mission under the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations of April 18, 1961.
… The Government of the Republic of Niger … authorizes the Government of the United States to exercise criminal jurisdiction over United States military personnel while in the Republic of Niger.
… The Embassy further proposes that the United States Department of Defense and United States personnel shall not be liable to pay any tax or similar charge assessed within the Republic of Niger and that the United States Department’of Defense and United States personnel may import into, export out of, and Use in the Republic of Niger any personal property, equipment, supplies, materiel, technology, training, or services in connection with activities under this Agreement. Such importation, exportation, and use shall be exempt from any inspection, license, other restrictions, customs, duties, taxes, or any other charges assessed within the Republic of Niger.
… The Embassy proposes that vehicles operated by or, at the time, exclusively for the United States Department of Defense may enter, exit, and move freely within the territory of the Republic of Niger, and that such vehicles (whether self-propelled or towed) shall not be subject to the payment of overland transit tolls. Aircraft owned or operated by or, at the time, exclusively for the United States Department of Defense shall not be subject to the payment of landing or parking fees at facilities owned and operated by the Government of the Republic of Niger. Aircraft owned and operated by or, at the time, exclusively for the United States Department of Defense shall not be subject to payment of navigation, overflight, terminal, or similar charges When in the territory of the Republic of Niger.
… Further, the Embassy proposes that the Parties waive any and all claims (other than contractual claims) against each other for damage to, loss, or destruction of the other’s property or injury or death to personnel of either Party’s armed forces or their civilian personnel arising out of the performance of their official duties in connection with activities under this Agreement.
…
Embassy of the United States of America
Niamey, July 6, 2012.

After almost 2 years of talking, the Zimbabwe gold-backed currency is finally upon us. Inflation is everywhere at the gas pump, at the food store, rent, prices are going up and up, affecting everyone and making the poor even poorer. In Zimbabwe, it has been going up for years given that the country has been under economic embargo for over 2 decades now. The traitors who toppled Robert Mugabe thought that by getting rid of him, the West would finally lift the embargo… alas, it has not been the case, and the country is still under embargo from the UK, US, and EU. Just at the beginning of March, the US slapped fresh sanctions against President Mnangagwa and some of his cronies, even though Mnangagwa has signed all sort of deals with the westerners upon his arrival in power [Is Zimbabwe the New Haiti?] and returned land [Zimbabwe to Return Seized Land to Foreigners].

As stated earlier, it is no secret that inflation is particularly high in Zimbabwe and has been for many years. Last week, the government of Zimbabwe has introduced a new gold-backed currency called ZiG, which stands for Zimbabwe Gold, in an effort to try to alleviate inflation, and stabilize the economy. The currency has been rolled out on Monday, and will replace the Zimbabwean dollar immediately; companies will be made to pay at least half of their taxes in ZiG. We hope that this will help the Zimbabwean economy to stay afloat. In honesty, isn’t this the way every currency should be: backed by gold and not just thin air? Upon its launch on Monday, the ZiG has fared well, and the hope is that it continues.
Excerpts below from the BBC. For a good read, check out also Business Insider.
=====

Zimbabwe has introduced a new gold-backed currency called ZiG – the name stands for “Zimbabwe Gold”.
It is the latest attempt to stabilise an economy that has lurched from crisis to crisis for the past 25 years.
Unveiling the new notes, central bank governor John Mushayavanhu said the ZiG would be structured, and set at a market-determined exchange rate. The ZiG replaces a Zimbabwean dollar, the RTGS, that had lost three-quarters of its value so far this year. Annual inflation in March reached 55% – a seven-month high.
Zimbabweans have 21 days to exchange old, inflation-hit notes for the new currency. However, the US dollar, which accounts for 85% of transactions, will remain legal tender and most people are likely to continue to prefer this.
The new ZiG banknotes come in denominations of between 1 and 200. Coins will also be introduced to overcome the shortage of US coins, which has seen people receive change in sweets, small chocolates and pens.
Mr Mushayavanhu said the new currency was being rolled out with immediate effect and banks must convert current Zimbabwe dollar balances to the ZiG. He committed to ensuring that the amount of local currency in circulation was backed by equivalent value in precious minerals – mainly gold – or foreign exchange, in order to prevent the currency losing value like its predecessors.
…

A few weeks ago, the son of Africa’s revered writer, Ngugi wa Thiong’o: world acclaimed Kenyan writer, took to X and wrote about his father being an abusive husband, “My father Ngugi wa Thiong’o physically abused my late mother. He would beat her up. Some of my earliest memories are of me going to visit her at my grandmother’s where she would seek refuge.” The tweet went viral, and took everyone by surprise. Surprise, because human tendency makes it so that we tend to place our heroes on pedestal as if they were no longer human; surprise, because Ngugi wa Thiong’o alongside Chinua Achebe is one of Africa’s greatest writers worthy of the Nobel prize of literature; surprise, because Ngugi wa Thiong’o work has been denouncing colonialism, imperialism, nepotism, neo-colonialism, and African governments’ repression and mismanagement, but never has he denounced the conditions of the African woman; lastly, surprise because, in Africa, and in Kikuyu culture particularly, it is not so common to air one’s dirty laundry in public, particularly against an elder. Sure enough, the son, Mukoma wa Ngugi responded to the backlash, “We cannot use African culture to hide atrocities,” he wrote on X. “My father beat up my mother. What is African about that?”
I, like so many, am against violence in general, and violence against women in particular. As we digest the news about Ngugi wa Thiong’o, is it not time for our acclaimed African writer who is in his twilight years to give us one masterpiece which focuses on patriarchy, women condition, and women in general, as an atonement? Is it not time for this to open up a dialogue?
Below is an excerpt from Al Jazeera. Enjoy, it is a nice read!
=====

On March 12, Mukoma wa Ngugi, the Kenyan American poet and author, who is the son of Ngugi wa Thiong’o, the famed writer widely seen as a giant of African literature, took to X, formerly Twitter, to allege that his father was an abusive husband. “My father Ngugi wa Thiong’o physically abused my late mother. He would beat her up. Some of my earliest memories are of me going to visit her at my grandmother’s where she would seek refuge.”
Mukoma’s tweet went viral and solicited hundreds of responses that exposed the long, dark shadow patriarchy continues to cast over many African societies. Sure, many commentators thanked Mukoma for sharing his account of a man who is not only his father, but an African cultural icon. Others, however, were less complimentary and appeared to be gravely offended by his openness. They accused him of embarrassing his father and seeking validation from Westerners.
… Ten days after his initial statement, on March 23, Mukoma responded to the criticism he received for speaking up for his mother. “We cannot use African culture to hide atrocities,” he wrote on X. “My father beat up my mother. What is African about that?” In another post, he described the culture of violence against women that underpins Kenyan society as a “patriarchal cancer”.

Ngugi is a literary genius, a storyteller par excellence and a respected revolutionary. Before there was the internet, video on-demand platforms, TV or even radio in most households, two African giants dominated African literature: Chinua Achebe, the Nigerian author, and, of course, Ngugi. From the 1960s, Achebe and Ngugi articulated African identity and consciousness amid the anti-colonial struggle. They stood up for the human rights of Africans with their words.
Through novels like Things Fall Apart and Arrow of God, to name a few, Achebe chronicled the impact of colonialism on Igbo culture, religion and sociopolitical systems. And in a Man of the People, he explored the failings of postcolonial leadership and states.

Ngugi, who went by the name James early in his career, also focused on African opposition to colonial rule. Weep not Child, for instance, deals with the so-called Mau Mau Uprising, while A grain of wheat looks at the state of emergency in Kenya’s struggle for independence (1952–60). Through these and other novels, Ngugi advocated for resistance against colonial oppression and repression in the independence era. In 1978, he was arrested and detained for a year without trial by the administration of former Kenyan President Jomo Kenyatta over a play titled Ngahlika Ndenda (I will marry when I want). Over the years, Ngugi was regularly harassed and victimised by authorities in Kenya for voicing his opposition to corruption, misrule and the abuse of power. He has stayed the course and today, at the age of 86, continues to advocate for freedom from neocolonialism and political oppression. With 13 honorary degrees from institutions around the world, as well as countless awards, including the 2022: PEN/Nabokov Award for Achievement in International Literature, Ngugi is a certified literary genius. But, for all of his achievements in the last 60 years, the famed author appears to have failed where it counted most: protecting African women.
He produced many timeless literary classics, and became a leading voice in the fight against colonialism and post-colonial repression, but according to his own son, could not liberate his dear wife, sons and daughters from the extreme ravages of toxic masculinity and domestic violence. Of course, in the wake of Mukoma’s public disclosures, Africans could choose to label Ngugi a flawed genius. He is, after all, human. They could – as many tried to do in lashing out at [Mukoma] – brush his alleged abuse of his wife under the carpet in the name of protecting his literary and revolutionary legacy. This would be an easy and convenient position to take.
But it wouldn’t be right.

… Ngugi, it seems, wanted women to experience liberty from colonialism and post-colonial subjugation, but remain bonded to the steely constraints of Kikuyu culture. … To his mind, it seems, there were limits to women’s human rights. For a long time, under the guise of tradition, African men have been allowed and even encouraged to discipline “their women” and children with violence [this does not apply to all African men]. Thus, many argue Ngugi is just a product of his times and what he is said to have done to his late wife should not be judged through a 21st-century progressive lens.
… Ngugi’s alleged violence is, unfortunately, a window to a continental (and, frankly global) problem. Hence, his son’s revelations should not become a point of contention. This should instead be a teaching moment.
… It is time to say enough is enough.

“How true! Life’s problems are like trees. We see the trunk, we see the branches and the leaves. But we can’t see the roots, hidden deep down under the ground. And yet it is their shape and nature and how far they dig into the slimy humus to search for water that we need to know. Then perhaps we would understand.”
Maryse Condé, Crossing the Mangrove

The great Guadeloupean writer, the Grande dame of Caribbean literature, Maryse Condé has transitioned to the land of our ancestors at the age of 90. Condé’s work has touched so many throughout the world, as it was a bridge between Africa, the Caribbean, and Europe. Her best work, Segu, has been one of my favorites. My first encounter with Maryse Condé’s work, was when I read her book “La Belle Créole.” Then I read Segu, and really that was it! I was sold… It was unforgettable, strong, and vivid. This book might actually be among the first historical fiction books written by a person of African descent on one of the ancient African kingdoms spanning several decades. Set in the 18th century, it followed the life of Dousika Traore, a royal adviser in an ancient historical kingdom based in Segu in modern-day Mali, torn apart by the arrival of the slave trade and Islam. It reminded me of the Alex Haley’s Kunta Kinte or Roots saga. It was deep, rich, and truly captivating.

In “I, Tituba: Black Witch of Salem,” Condé told the story of a slave who was one of the first women to be accused of witchcraft during the 1692 Salem witch trials. It was based on the story of an American slave who was tried for witchcraft. Honestly, up until then, I could not fathom that a Black woman could have been on trial back then in the United States; but in reality, given how Africans were uprooted from the continent, and their religion, and spirituality, it should not have come as a surprise.
I read her other book, The last of the African Kings which is a fictional account following King Behanzin’s offsprings and entourage when he was in exile in Martinique, and their lives in the caribbeans and then the United States, after the French deported him there. It skillfully intertwined the themes of exile, memory, hope, loss, with Africa always in the background.

After that, I read her other books A Season in Rihata, The Crossing of the Mangrove, La Vie Scélérate (Tree of Life: A Novel of the Caribbean), Desiderada.
Her themes always embraced motherhood, femininity, race relations, slavery, the Caribbeans, and Africa. Her novels drew upon African and Caribbean history. She has written over 20 novels,
Throughout her life, she was awarded France’s Legion of Honour in 2004, and twice nominated for the International Booker Prize – first for her entire body of work in 2015, then in 2023 for her final novel, The Gospel According to the New World. In 2018, she won an award set up in place of the Nobel Prize in Literature, which was engulfed in scandal. Condé was the first and remains the only winner of the New Academy Prize in Literature, whose judges praised the way she “describes the ravages of colonialism and post-colonial chaos in a language which is both precise and overwhelming“.
The excerpts below are from the Guardian.
=====

… Born Maryse Boucolon in Guadeloupe in 1934, the youngest of eight children, Condé described herself as a “spoilt child … oblivious to the outside world”. Her parents, she told the Guardian, never taught her about slavery and “were convinced France was the best place in the world”. She went to Paris at 16 for her education, but was expelled from school after two years: “When I came to study in France I discovered people’s prejudices. People believed I was inferior just because I was black. I had to prove to them I was gifted and to show to everybody that the colour of my skin didn’t matter – what matters is in your brain and in your heart.”
Studying at the Sorbonne, she began to learn about African history and slavery from fellow students and found sympathy with the Communist movement. She became pregnant after an affair with Haitian activist Jean Dominique. In 1958, she married the Guinean actor Mamadou Condé, a decision she later admitted was a means of regaining status as a black single mother. Within months their relationship was strained, and Condé moved to the Ivory Coast, spending the next decade in various African countries including Guinea, Senegal, Mali and Ghana, mixing with Che Guevera, Malcolm X, Julius Nyerere, Maya Angelou, future Ivory Coast president Laurent Gbagbo and Senegalese film-maker and author Ousmane Sembène.

Unable to speak local languages and presumed to hold francophile sympathies, Condé struggled to find her place in Africa. “I know now just how badly prepared I was to encounter Africa,” she would later say. “I had a very romantic vision, and I just wasn’t prepared, either politically or socially.” She remained outspoken until she was accused of subversive activity in Ghana and deported to London, where she worked as a BBC producer for two years. She eventually returned to France and earned her MA and PhD in comparative literature at Paris-Sorbonne University in 1975.
Her debut novel, Hérémakhonon, was published in 1976, with Condé saying she waited until she was nearly 40 because she “didn’t have confidence in myself and did not dare present my writing to the outside world”. The novel follows a Paris-educated Guadeloupean woman, who realises that her struggle to locate her identity is an internal journey, rather than a geographical one. Condé later recalled the Ghanaian author Ama Ata Aidoo telling her: “Africa … has codes that are easy to understand. It’s because you’re looking for something else … a land that is a foil that would allow you to be what you dream of being. And on that level, nobody can help you.” “I think she may have been right,” Condé later wrote.
… She gained prominence as a contemporary Caribbean writer with her third novel, Segu, in 1984. The novel follows the life of Dousika Traore, a royal adviser in the titular African kingdom in the late-18th century, who must deal with encroaching challenges from religion, colonisation and the slave trade over six decades. It was a bestseller and praised as “the most significant novel about black Africa published in many a year” by the New York Times.